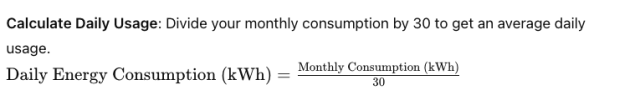How To Calculate Solar Panel Requirement?
Determining the optimal number of solar panels for your energy needs involves a careful assessment of various factors, including your average energy consumption, the wattage of the solar panels, available roof space, and your geographical location. This guide provides step-by-step instructions on estimating the number of panels needed and discusses the concept of system sizing, its impact on energy production, and cost-effectiveness.
Table of Contents
- 1 Understanding Energy Consumption Patterns
- 1.1 Analyzing Monthly and Annual Energy Usage
- 1.2 Calculating Solar Panel Wattage Based on Energy Needs
- 1.3 Assessing Roof Suitability and Available Space
- 1.4 Considering Factors Like Shading and Orientation
- 1.5 Balancing System Size with Budget and Incentives
- 1.6 Using Online Solar Calculators
- 1.7 Optimizing Solar Panel Placement for Maximum Efficiency
- 1.8 The Role of Battery Storage in Solar System Sizing
- 1.9 System Sizing Calculation
Understanding Energy Consumption Patterns
Analyzing Monthly and Annual Energy Usage
- Review Utility Bills: Look at the last 12 months of electricity bills to determine your average monthly and annual energy consumption in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
- Identify Peak Usage: Note the months with the highest energy usage to understand your peak demand.
Daily Energy Consumption
Calculating Solar Panel Wattage Based on Energy Needs
Understanding Panel Wattage
- Standard Panel Wattage: Most residential solar panels have wattages between 250W and 400W.
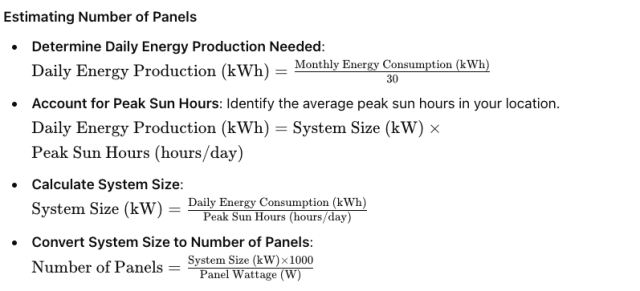
Estimating Number of Panels
Assessing Roof Suitability and Available Space
Roof Size and Orientation
- Measure Roof Area: Calculate the total available area for panel installation.
- Determine Orientation and Tilt: South-facing roofs with a tilt angle equal to your latitude are ideal for maximum solar exposure.
Shading and Structural Integrity
- Check for Shading: Identify any obstructions that may cast shadows on the panels.
- Assess Structural Integrity: Ensure your roof can support the additional weight of the solar panels.
Considering Factors Like Shading and Orientation
Minimizing Shading Impact
- Tree Trimming: Trim trees that could cause shading.
- Panel Placement: Position panels to avoid shading from chimneys, vents, and other obstructions.
Optimal Orientation and Tilt
- Orientation: Panels should ideally face south in the Northern Hemisphere and north in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Tilt Angle: Adjust the tilt angle to match your latitude for optimal sunlight capture.
Balancing System Size with Budget and Incentives
Cost Considerations
- Initial Investment: Larger systems have higher upfront costs.
- Long-term Savings: More panels can result in greater savings on electricity bills over time.
Incentives and Rebates
- Federal and State Incentives: Check for available incentives, rebates, and tax credits to reduce the cost of your solar installation.
- Net Metering: Understand how net metering policies in your area can impact the financial benefits of your system.
Using Online Solar Calculators
Enter your location, energy consumption, roof details, and panel specifications. Review the estimated number of panels, system size, energy production, and cost savings.
Optimizing Solar Panel Placement for Maximum Efficiency
Panel Placement Strategies
- Uniform Spacing: Ensure even spacing between panels to prevent shading.
- Adjustable Mounts: Use adjustable mounts to optimize the tilt angle seasonally.
Performance Monitoring
- Install Monitoring Systems: Track the performance of your solar system to identify and address any issues promptly.
The Role of Battery Storage in Solar System Sizing
Benefits of Battery Storage
- Energy Independence: Store excess energy for use during nighttime or cloudy days.
- Backup Power: Provide backup power during grid outages.
Sizing Battery Storage
- Assess Storage Needs: Determine how much storage capacity you need based on your energy consumption patterns and backup power requirements.
- Integrate with Solar System: Ensure your battery storage system is compatible with your solar panels and inverter.
System Sizing Calculation
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Monthly Energy Consumption | 900 kWh |
| Daily Energy Consumption | 30 kWh |
| Average Peak Sun Hours | 5 hours/day |
| Required System Size | 6 kW |
| Panel Wattage | 300W |
| Number of Panels | 20 panels (6000W / 300W per panel) |
Conclusion
Determining the optimal number of solar panels for your energy consumption involves understanding your energy needs, calculating the required system size, assessing your roof’s suitability, and considering factors like shading and orientation. Balancing your system size with your budget and available incentives is crucial for maximizing the benefits of solar energy. Using online tools and professional advice can help you design an efficient and cost-effective solar power system.
FAQs
1. How do I determine my average energy consumption?
Review your utility bills to find your average monthly and annual energy usage in kWh.
2. What factors affect the number of solar panels I need?
Factors include your energy consumption, panel wattage, roof space, location, shading, and orientation.
3. How can I maximize the efficiency of my solar panels?
Optimize panel placement, minimize shading, and adjust the tilt angle to match your latitude.
4. Is battery storage necessary for my solar system?
Battery storage is not necessary but can provide energy independence and backup power.
5. What incentives are available for solar installations?
Check federal, state, and local incentives, rebates, and tax credits to reduce the cost of your solar installation.