how to make a solar panel out of aluminum foil
The internet is full of DIY projects and life hacks, but not all of them are based on sound science. One such myth that has gained some attention is the idea that aluminum foil can be used to create a functional solar panel. This blog post aims to debunk this misconception by explaining the science behind solar panel technology, the essential components required for efficient energy conversion, and why aluminum foil simply cannot perform the necessary functions of a solar panel.
Table of Contents
- 1 The Science of Solar Panels and Their Components
- 2 The Limitations of Aluminum Foil as a Solar Panel Material
- 3 The Importance of Semiconductors in Solar Energy Conversion
- 4 The Role of Anti-Reflective Coatings and Encapsulation
- 5 The Challenges of Building a Solar Panel at Home
- 6 The Environmental Impact of DIY Solar Panels
- 7 The Potential for DIY Solar Panel Projects to Be Harmful or Dangerous
- 8 The Importance of Professional Solar Panel Installation
- 9 Encouraging Readers to Support Sustainable Energy Initiatives Through Responsible Practices
- 10 The Future of Solar Technology and Its Advancements
- 11 Table: Comparison of Aluminum Foil and Solar Panel Materials
- 12 FAQ Section
- 13 Conclusion
The Science of Solar Panels and Their Components
What Are Solar Panels?
- Definition: Solar panels are devices that convert sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic (PV) effect. This process involves absorbing sunlight and generating an electric current, which can be used to power electrical devices or stored for later use.
Essential Components of Solar Panels:
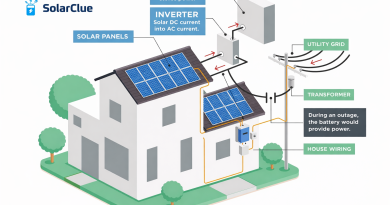
- Solar Cells: The core component, usually made of semiconductor materials like silicon, that converts sunlight into electricity.
- Encapsulation: Protective layers that safeguard the solar cells from environmental damage.
- Anti-Reflective Coatings: Layers that reduce the reflection of sunlight, ensuring more light is absorbed by the solar cells.
- Junction Box: Houses the electrical connections and protects them from weather conditions.
- Glass and Frame: The outer structure that protects the solar cells and provides durability.
The Limitations of Aluminum Foil as a Solar Panel Material
Conductivity vs. Photovoltaic Effect:
- Aluminum Foil’s Role: Aluminum foil is a good conductor of electricity, but it does not possess the properties necessary to convert sunlight into electricity. Conducting electricity is different from generating it.
- Lack of Semiconducting Properties: Unlike silicon or other semiconductor materials, aluminum foil does not have the ability to generate an electric current when exposed to sunlight.
Reflectivity:
- High Reflectance: Aluminum foil reflects most of the sunlight that hits it, which is counterproductive in a solar panel where maximum light absorption is required.
The Importance of Semiconductors in Solar Energy Conversion
What Are Semiconductors?
- Definition: Semiconductors are materials that have electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Silicon is the most commonly used semiconductor in solar cells.
- Role in Solar Panels: Semiconductors absorb photons from sunlight and release electrons, creating an electric current.
Why Aluminum Foil Can’t Replace Semiconductors:
- Lack of Photovoltaic Properties: Aluminum foil cannot absorb sunlight and generate an electric current like semiconductor materials can.
The Role of Anti-Reflective Coatings and Encapsulation
Anti-Reflective Coatings:
- Purpose: These coatings are applied to the surface of solar cells to reduce the amount of light that is reflected away and increase the amount of light that is absorbed.
- Importance: Without anti-reflective coatings, much of the sunlight would be lost, reducing the efficiency of the solar panel.
Encapsulation:
- Protection: Encapsulation layers protect the solar cells from moisture, dust, and mechanical damage, ensuring long-term durability and efficiency.
- Aluminum Foil Limitation: Aluminum foil cannot serve as an effective encapsulating material due to its lack of transparency and inability to protect the cells from environmental factors.
The Challenges of Building a Solar Panel at Home
Complex Manufacturing Process:
- Precision and Technology: Manufacturing a solar panel involves precise processes like doping of semiconductors, application of anti-reflective coatings, and encapsulation, which require specialized equipment and knowledge.
- DIY Limitations: Attempting to build a solar panel at home without proper materials and tools can result in a non-functional and potentially hazardous setup.
The Environmental Impact of DIY Solar Panels
Potential Harm:
- Substandard Materials: Using inappropriate materials like aluminum foil can lead to ineffective solar panels, resulting in wasted resources and potentially harmful waste if not disposed of properly.
- Energy Waste: Inefficient DIY panels may require more energy to manufacture than they can ever produce, negating the environmental benefits of solar power.
The Potential for DIY Solar Panel Projects to Be Harmful or Dangerous
Safety Concerns:
- Electrical Hazards: Improperly constructed solar panels can pose serious electrical risks, including shocks, short circuits, and fires.
- Toxic Materials: Some DIY approaches might involve using materials that are not environmentally friendly or safe, leading to potential health risks.
The Importance of Professional Solar Panel Installation
Why Professional Installation Matters:
- Compliance with Standards: Professional installers ensure that the solar panel system meets all safety and performance standards.
- Maximizing Efficiency: Proper installation ensures that the panels are optimally positioned and connected, maximizing energy output.
- Long-Term Reliability: Professionally installed systems are more likely to be durable and efficient over the long term.
Encouraging Readers to Support Sustainable Energy Initiatives Through Responsible Practices
Invest in Quality:
- Supporting Renewable Energy: Instead of trying ineffective DIY methods, consider supporting sustainable energy initiatives by investing in quality solar panel systems from reputable manufacturers.
- Education and Awareness: Understanding the science behind solar technology can help debunk myths and promote responsible energy practices.
The Future of Solar Technology and Its Advancements
Ongoing Research:
- New Materials: Researchers are continually developing new materials that could increase the efficiency and reduce the cost of solar panels.
- Innovations: Future advancements may include flexible solar panels, transparent solar cells, and integrated solar solutions for various applications.
Table: Comparison of Aluminum Foil and Solar Panel Materials
| Feature | Aluminum Foil | Solar Panel Materials (e.g., Silicon) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | High | Moderate |
| Photovoltaic Properties | None | High |
| Light Absorption | Low (High Reflectance) | High |
| Durability | Low (Easily Damaged) | High (Encapsulated and Protected) |
| Suitability for Solar Panels | Not Suitable | Highly Suitable |
FAQ Section
- Can aluminum foil be used to make a solar panel?
- No, aluminum foil lacks the photovoltaic properties necessary to convert sunlight into electricity. It can conduct electricity but cannot generate it.
- What are the essential components of a real solar panel?
- Real solar panels consist of semiconductor materials like silicon, anti-reflective coatings, encapsulation layers, a protective glass cover, and a junction box for electrical connections.
- Why is aluminum foil not effective for solar panels?
- Aluminum foil reflects most sunlight, has no photovoltaic properties, and cannot replace the complex materials and processes involved in manufacturing efficient solar panels.
- Is it possible to build a functional solar panel at home?
- While it’s possible to create a basic solar cell with specific materials, building a fully functional and efficient solar panel requires precise manufacturing processes and materials that are not easily accessible for DIY projects.
- What are the risks of attempting to build a solar panel using inappropriate materials?
- Using inappropriate materials like aluminum foil can result in non-functional panels, wasted resources, potential electrical hazards, and environmental harm.
Conclusion
The myth that aluminum foil can be used to create a functional solar panel is simply not true. Understanding the science behind solar panel technology highlights the importance of using appropriate materials and professional installation to ensure safety, efficiency, and sustainability. As solar technology continues to advance, it’s essential to rely on scientifically sound practices and support renewable energy initiatives through responsible choices.