On-Grid Solar System: Everything You Need to Know
The increasing demand for renewable energy has given rise to various innovative technologies, one of which is the on-grid solar system. With the sun’s energy being the most abundant and cleanest source of power, harnessing it through solar systems has gained immense popularity in recent years. In this blog, we will explore the concept of on-grid solar systems and shed light on their benefits, working mechanism, and importance in the transition towards a sustainable future.
Table of Contents
Understanding the On-Grid Solar System:
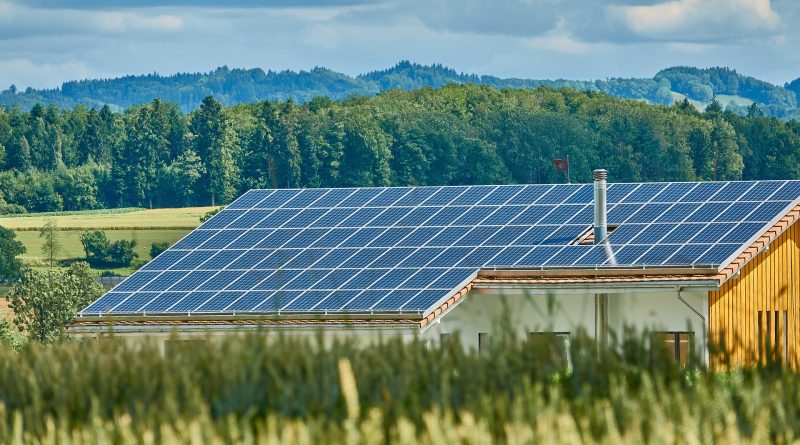
The on-grid solar system, also known as a grid-tied or grid-connected system, is a solar power setup that is directly connected to the utility grid. Unlike off-grid systems that require batteries to store excess energy, on-grid systems allow homeowners and businesses to generate electricity from solar panels while simultaneously being connected to the grid. This seamless integration offers several advantages and has become a popular choice for those looking to tap into renewable energy resources.
The Benefits of On-Grid Solar Systems:
1. Reduced Utility Bills: One of the primary advantages of on-grid solar systems is their ability to offset or even eliminate monthly electricity bills. By generating their own electricity, individuals and businesses can significantly reduce their dependence on the grid, resulting in substantial cost savings over time.
2. Net Metering: On-grid solar systems offer the option of net metering, allowing surplus electricity produced by solar panels to be fed back into the grid. In return, this excess energy is credited to the owner’s account, offsetting future electricity consumption or even generating income in some cases.
3. Environmentally Friendly: As a clean and renewable energy source, solar power helps to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change. On-grid systems make a substantial contribution towards sustainable development by reducing the reliance on fossil fuels and promoting a greener future.
How Does an On-Grid Solar System Work?
An on-grid solar system comprises three main components: solar panels, an inverter, and the utility grid.
1. Solar Panels: Solar panels, often mounted on rooftops or open areas, consist of photovoltaic (PV) cells that convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity. These panels are typically made of silicon-based materials that efficiently capture sunlight and produce an electric current.
2. Inverter: The direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels needs to be converted into alternating current (AC) electricity to be compatible with the utility grid and household appliances. Inverters perform this conversion, ensuring a seamless flow of electricity from the solar panels to the grid.
3. Utility Grid: The utility grid, operated by local electricity providers, acts as a backup power source for on-grid solar systems. During periods of low energy production or high energy demand, the system can draw electricity from the grid. Conversely, when there is excess solar power, it can be fed back into the grid.
The Importance of On-Grid Solar Systems:
1. Increased Renewable Energy Penetration: On-grid solar systems have contributed significantly to increasing the overall penetration of renewable energy in the electricity generation mix. As more homes and businesses adopt on-grid systems, the demand for fossil fuel-based electricity decreases, leading to a cleaner and more sustainable energy supply.
2. Grid Stability and Demand Management: On-grid solar systems play a crucial role in maintaining the stability of the utility grid by reducing peak demand and load fluctuations. The excess solar power generated during non-peak hours can be utilized to meet peak demands, reducing stress on the grid and enhancing overall reliability.
3. Promotion of Green Technologies: The prominence of on-grid solar systems fosters innovation and investment in solar technology. Increased demand for solar panels and inverters encourages manufacturers to develop more efficient and cost-effective solutions, driving down prices and making solar energy more accessible to the masses.
Conclusion:
On-grid solar systems offer a compelling solution to the increasing demand for clean, renewable energy. With their ability to offset electricity bills, leverage net metering, and reduce environmental impact, these systems have gained significant popularity. By understanding the working mechanism and benefits of on-grid solar systems, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions about adopting this technology and contribute towards a sustainable future. Embracing on-grid solar systems not only aids in cost savings but also plays a part in reducing carbon emissions and shaping a greener world for generations to come.
Ready to embrace a greener future? Explore the benefits of on-grid solar systems with SolarClue® today! Let’s power a sustainable tomorrow together.
Frequently Asked Questions
An on-grid solar system is a setup where solar panels are connected to the local utility grid, allowing excess energy to be fed back into the grid.
The solar panels generate electricity, and the inverter converts it into usable AC power. Excess energy is sent to the grid, and you draw power from the grid when needed.
Benefits include reduced electricity bills, potential income from excess energy production, and contributing to a more sustainable energy grid.
Typically, no. On-grid systems use the grid as a virtual battery, eliminating the need for physical storage.
A certified installer will handle the grid connection process, ensuring compliance with local regulations and safety standards.
No, for safety reasons. When the grid goes down, on-grid systems shut off to prevent backfeeding electricity into the grid.
They are most effective in areas with a reliable and well-maintained electrical grid.
Regular cleaning of solar panels and occasional checks by a professional are typically sufficient.
While primarily designed for grid-tied operation, it is possible to incorporate backup solutions for limited off-grid functionality.
Many regions offer incentives, tax credits, or feed-in tariffs to encourage the adoption of on-grid solar systems, making it a financially attractive option.