How Many kWh Does A Solar Panel Produce Per Day?
Estimating solar panel energy production is essential for understanding the potential benefits and savings of a solar power system. This blog covers the key factors affecting solar panel output, including panel wattage, peak sun hours, solar irradiance, and weather conditions. It provides calculations and examples to estimate daily, monthly, and annual electricity generation and discusses the concept of solar energy potential across different regions.
Table of Contents
- 1 Understanding Solar Panel Wattage and Energy Production
- 1.1 Factors Affecting Solar Energy Output
- 1.2 Calculating Energy Generation Based on Peak Sun Hours
- 1.3 Estimating Electricity Production for Different Seasons
- 1.4 The Role of Energy Storage in Maximizing Solar Utilization
- 1.5 Comparing System Output to Average Household Consumption
- 1.6 The Impact of Panel Orientation and Tilt on Energy Production
- 1.7 Real-World Factors Affecting Solar Panel Performance
- 1.8 Optimizing Solar Panel Systems for Maximum Energy Yield
- 1.9 Conclusion
- 1.10 Factors Affecting Solar Panel Output
- 1.11 FAQs
Understanding Solar Panel Wattage and Energy Production
Solar Panel Wattage
- Definition: Solar panel wattage is the maximum power output a panel can produce under standard test conditions (STC).
- Common Wattages: Residential panels typically range from 250 to 400 watts.
Energy Production
- Energy Output: Measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), it depends on the panel’s wattage and the amount of sunlight it receives.
Factors Affecting Solar Energy Output
Sunlight
- Peak Sun Hours: The number of hours per day when sunlight intensity is at least 1,000 watts per square meter. This varies by location and season.
Temperature
- Temperature Coefficient: Higher temperatures can reduce panel efficiency. Most panels have a temperature coefficient indicating performance loss per degree Celsius increase above 25°C.
Shading
- Impact: Even partial shading can significantly reduce output, as it can affect the entire string of panels.
Solar Irradiance
- Definition: The power per unit area received from the sun, measured in watts per square meter. Higher irradiance leads to higher energy production.
Weather Conditions
- Cloud Cover: Reduces the amount of sunlight reaching the panels.
- Snow and Rain: Can block sunlight or clean the panels, affecting performance.
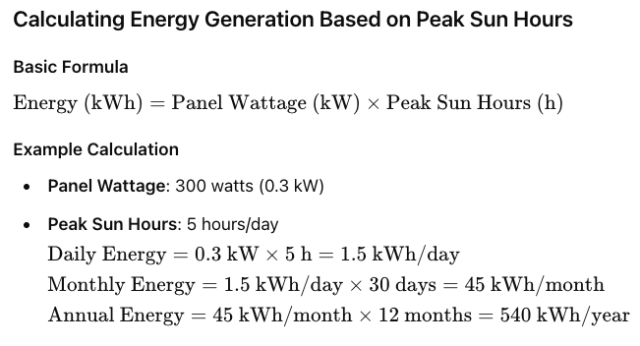
Calculating Energy Generation Based on Peak Sun Hours
Estimating Electricity Production for Different Seasons
- Summer: Longer days and higher peak sun hours increase production.
- Winter: Shorter days and lower peak sun hours decrease production.
The Role of Energy Storage in Maximizing Solar Utilization
- Battery Storage: Stores excess energy for use during non-sunlight hours or peak demand times.
- Grid-Tied Systems: Surplus energy is fed back into the grid, and deficit energy is drawn from it.
Comparing System Output to Average Household Consumption
- Average Household Consumption: Typically ranges from 8,000 to 12,000 kWh per year.
- System Sizing: Ensure the solar system meets or exceeds household energy needs based on consumption patterns.
The Impact of Panel Orientation and Tilt on Energy Production
- Optimal Orientation: Panels should face true south in the Northern Hemisphere and true north in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Optimal Tilt: Generally equal to the latitude of the location for maximum annual production.
Real-World Factors Affecting Solar Panel Performance
- Dust and Dirt: Regular cleaning can maintain efficiency.
- Degradation: Panels lose efficiency over time, typically around 0.5% to 1% per year.
- Bird Droppings and Debris: Can block sunlight and should be removed promptly.
Optimizing Solar Panel Systems for Maximum Energy Yield
- Regular Maintenance: Clean panels, check connections, and monitor performance.
- Monitoring Systems: Use software to track energy production and detect issues.
- Professional Installation: Ensure panels are installed correctly for optimal performance.
Conclusion
Understanding the factors affecting solar panel energy production and how to calculate and estimate output is crucial for maximizing the benefits of a solar power system. By considering panel wattage, peak sun hours, solar irradiance, and weather conditions, and utilizing tools and software for precise estimation, you can optimize your solar panel system for maximum energy yield and efficiency.
Here at SolarClue®, we offer a smart, practical, and “beautiful” solution. You will be answered for all the questions related to Solar.
We provide all kinds of brands that are the Best Solar panels in India.
If you are the one who is planning for the solar power system. Don’t hesitate to contact our team!
Looking forward to empowering you with solar energy, just like hundreds of our other clients!
Factors Affecting Solar Panel Output
| Factor | Description | Impact on Output |
|---|---|---|
| Panel Wattage | Maximum power output under standard test conditions | Higher wattage = more energy |
| Peak Sun Hours | Hours per day with sunlight intensity of 1,000 W/m² | More peak sun hours = more energy |
| Solar Irradiance | Power per unit area received from the sun (W/m²) | Higher irradiance = more energy |
| Temperature | Affects panel efficiency, higher temps reduce output | Higher temperatures = less energy |
| Shading | Obstructions blocking sunlight | Shading = significantly less energy |
| Weather Conditions | Cloud cover, rain, snow affecting sunlight | Variable impact |
| Panel Orientation | Direction panels face relative to the sun | Optimal orientation = more energy |
| Panel Tilt | Angle of panels relative to horizontal | Optimal tilt = more energy |
FAQs
1. What are peak sun hours?
Peak sun hours refer to the number of hours per day when sunlight intensity is at least 1,000 watts per square meter.
2. How do I calculate the energy production of my solar panels?
Use the formula: Energy (kWh) = Panel Wattage (kW) × Peak Sun Hours (h).
3. What factors affect solar panel efficiency?
Factors include sunlight, temperature, shading, solar irradiance, and weather conditions.
4. How does panel orientation affect energy production?
Panels should face true south in the Northern Hemisphere and true north in the Southern Hemisphere for optimal energy production.
5. Why is energy storage important for solar systems?
Energy storage allows excess energy to be stored for use during non-sunlight hours or peak demand times, maximizing solar utilization.