On-Grid Solar System: Unlocking Key Insights
Solar energy is gaining popularity as an efficient and sustainable source of power. While most people are familiar with off-grid solar systems, on-grid solar systems offer a remarkable solution for homeowners and businesses alike. This blog aims to explore the benefits, working principles, and applications of on-grid solar systems, shedding light on an alternative energy solution that you may not have known about.
What is an On-Grid Solar System?
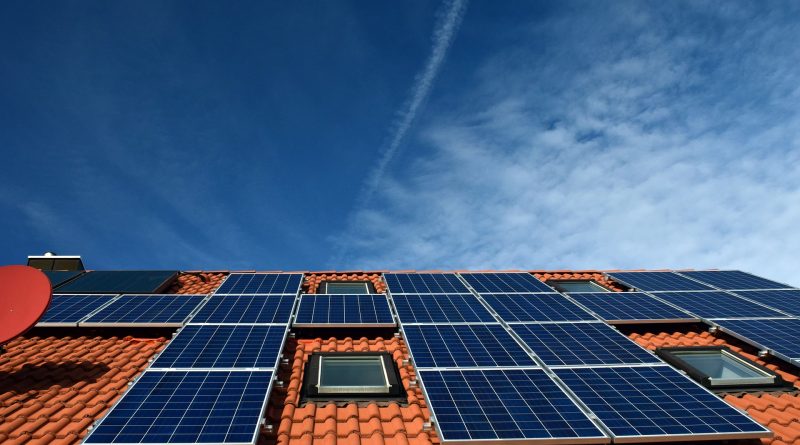
An on-grid solar system, also known as a grid-tie or grid-connected system, is a solar power system that is directly connected to the local electric grid. Unlike off-grid systems, which rely solely on solar energy and require battery storage, on-grid solar systems work in tandem with the existing electrical infrastructure. These systems generate electricity using photovoltaic (PV) panels, convert it to alternating current (AC) using inverters, and deliver it to the grid.
The Key Components
To understand the working of an on-grid solar system, it is important to familiarize yourself with its key components:
1. PV Panels:
The heart of any solar system, PV panels contain an array of solar cells that convert sunlight into electricity. These panels are typically installed on rooftops or open areas with optimal exposure to sunlight.
2. Inverters:
Inverters play a critical role in converting the direct current (DC) generated by PV panels into the alternating current (AC) used in homes and businesses. These devices are responsible for synchronizing the solar system with the grid.
3. Net Meter:
A net meter measures the amount of electricity produced by the solar system and the amount consumed from the grid. It allows for the seamless integration of the solar-generated electricity and the grid power, ensuring accurate billing and a balance between energy production and consumption.
How Does it Work?
The functioning of an on-grid solar system can be summarized into three main steps:
1. Solar Power Generation:
When sunlight falls on the PV panels, it activates the solar cells, initiating the process of electricity generation. The panels absorb photons from the sunlight, which dislodge electrons from atoms, creating a flow of DC electricity.
2. Electricity Conversion:
The DC electricity generated by the solar panels is passed through the inverters, which convert it into AC electricity. This conversion is necessary since most household appliances and electrical systems run on AC power.
3. Power Injection into the Grid:
After the electricity conversion, the AC power is then fed into the existing electrical grid. The solar system, working in parallel with the grid, provides power to the premises whenever the demand exceeds the solar generation. Conversely, during periods of excess solar power, the surplus energy is injected back into the grid through the net meter, earning credits with the utility company.
Advantages of On-Grid Solar Systems
Now that we have a good understanding of how on-grid solar systems operate, let’s explore the benefits they offer:
1. Cost Savings:
One of the most significant advantages of on-grid solar systems is their ability to save you money on electricity bills. By generating your own power, you can offset a portion or even the entirety of your electricity consumption from the grid, ultimately reducing your utility bills.
2. Return on Investment:
Investing in an on-grid solar system is not only an environmentally responsible decision but also a financially sound one. The excess electricity produced by your solar system can be fed back into the grid, allowing you to earn credits or even receive payments from your utility company through net metering or feed-in tariffs.
3. Grid Reliability:
Unlike off-grid solar systems that rely solely on solar power and battery storage, on-grid solar systems offer the advantage of grid reliability. During periods of low solar generation, such as cloudy days or at night, the system can draw power from the grid, ensuring a consistent and uninterrupted electricity supply.
4. Environmental Benefits:
By harnessing solar power, on-grid solar systems significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. This renewable energy source assists in combating climate change and contributes to a greener and healthier planet.
Applications of On-Grid Solar Systems
On-grid solar systems find applications in various sectors, including residential, commercial, and industrial. Some common applications include:
1. Residential:
Homeowners can install on-grid solar systems to reduce electricity bills, increase their homes’ value, and contribute to a sustainable future. The excess electricity generated during the day can be used to power homes at night or support the grid.
2. Commercial Buildings:
Businesses can adopt on-grid solar systems to save on operating costs, demonstrate corporate social responsibility, and establish a green business reputation. Large rooftops and open spaces in commercial buildings offer ample opportunities for solar panel installation.
3. Industrial Sector:
Industries, such as manufacturing plants and warehouses, can integrate on-grid solar systems to lower energy costs, reduce their carbon footprint, and comply with sustainability regulations. These systems can deliver significant financial savings for energy-intensive operations.
Conclusion
On-grid solar systems serve as an efficient and cost-effective solution for harnessing solar energy while leveraging the existing electrical infrastructure. With their cost-saving potential, return on investment, and environmental benefits, these systems are becoming increasingly popular in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. By adopting on-grid solar systems, individuals and businesses can contribute towards a greener future while enjoying the advantages of reduced electricity bills and a reliable power supply. So, why not consider going solar and be a part of the clean energy revolution?
Ready to embrace on-grid solar efficiency? Explore the future with SolarClue®. Visit our website now to unlock a range of on-grid solar solutions tailored to elevate your energy experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
On-grid systems are connected to the main power grid, while off-grid operates independently.
On-grid systems offer continuous power supply and the potential for surplus energy sales.
Yes, on-grid systems are adaptable for residential use, providing reliable and cost-effective energy.
SolarClue® integrates advanced technologies to enhance the efficiency and reliability of on-grid solar systems.
Routine checks and occasional cleaning are typically sufficient to maintain optimal on-grid solar system performance.
While possible, it may require system modifications; consult with SolarClue® experts for guidance.
Typically, they do not, as safety measures disconnect them during outages to protect utility workers.
In many regions, there are tax incentives and rebates for on-grid solar installations.
Factors include location, energy needs, and the desire for energy independence; SolarClue® can help you decide.
On-grid solar reduces reliance on traditional energy sources, lowering the carbon footprint and promoting eco-friendliness.