Diverse Types of Solar Mounting Structures for Various Needs
Table of Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Section 1: Fixed-Tilt Solar Mounts
- 3 Section 2: Tracking Solar Mounts
- 4 Section 3: Roof-Mounted Structures
- 5 Section 4: Ground-Mounted Structures
- 6 Section 5: Floating Solar Structures
- 7 Section 6: Solar Carports
- 8 Section 7: Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV)
- 9 Section 8: Customized Mounting Solutions
- 10 Conclusion
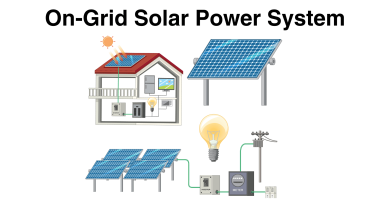
Introduction
As solar energy continues to gain prominence, the diversity of solar mounting structures has become crucial to accommodate various needs and environments. In this blog post, we will explore the different types of solar mounting structures, highlighting their unique features and applications.
Section 1: Fixed-Tilt Solar Mounts
1.1 Overview
Fixed-tilt solar mounts are stationary structures that hold solar panels at a fixed angle. So this simplicity makes them cost-effective and easy to install.
1.2 Applications
Ideal for regions with consistent sunlight, fixed-tilt mounts are commonly used in utility-scale solar farms and commercial installations.
Section 2: Tracking Solar Mounts
2.1 Single-Axis Tracking
Tracking solar mounts follow the sun’s path throughout the day, maximizing energy capture. Single-axis tracking adjusts panels along one axis.
2.2 Dual-Axis Tracking
Dual-axis tracking systems optimize solar panel orientation on both horizontal and vertical axes, ensuring maximum exposure to sunlight.
2.3 Applications
Tracking mounts are beneficial in areas with variable sunlight, enhancing energy production for residential and commercial installations.
Section 3: Roof-Mounted Structures
3.1 Ballasted Roof Mounts
Ballasted roof mounts are non-penetrating structures suitable for flat roofs. Therefore, They use weights to secure solar panels in place without penetrating the roof surface.
3.2 Penetrating Roof Mounts
Penetrating roof mounts attach directly to the roof structure. So they providing a secure and durable option for pitched roofs.
3.3 Applications
Roof-mounted structures are popular for residential and commercial buildings. This helps in utilizing available roof space for solar installations.
Section 4: Ground-Mounted Structures
4.1 Pole Mounts
Pole mounts are elevated structures with solar panels mounted on poles. So they are versatile and can be installed in various terrains.
4.2 Tilted Ground Mounts
Tilted ground mounts raise solar panels at an angle, optimizing energy capture. They are suitable for sites with uneven terrain.
4.3 Applications
Ground-mounted structures are commonly used in residential settings, agricultural lands, and remote areas where roof installations are impractical.
Section 5: Floating Solar Structures
5.1 Overview
You can design floating solar structures for installing solar energy on bodies of water, such as ponds, lakes, or reservoirs
5.2 Applications
Floating solar structures are ideal for water bodies, providing an innovative solution for energy generation without occupying land space.
Section 6: Solar Carports
6.1 Overview
Solar carports serve a dual purpose, providing shelter for vehicles while also generating solar energy.
6.2 Applications
Commonly used in commercial and industrial settings, solar carports offer a sustainable solution for parking areas.
Section 7: Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV)
7.1 Overview
BIPV integrates solar panels seamlessly into building structures, serving both aesthetic and functional purposes.
7.2 Applications
Residential and commercial construction utilizes BIPV. This blends solar technology with architectural design.
Section 8: Customized Mounting Solutions
8.1 Tailored Solutions
In certain cases, customized mounting solutions are designed to meet specific project requirements, considering factors like location, climate, and space constraints.
8.2 Applications
Customized mounting solutions are versatile and can be adapted to a range of environments. So it makes them suitable for unique solar projects.
Conclusion
The diverse types of solar mounting structures cater to a wide range of needs and environments, reflecting the adaptability and versatility of solar technology. Whether in utility-scale solar farms, residential rooftops, or innovative floating installations, the choice of mounting structure plays a pivotal role in optimizing energy capture and ensuring the success of solar projects. As the solar industry continues to evolve, the availability of varied mounting options underscores the commitment to making solar energy accessible and effective across diverse applications.