Heat Pump Working Principle
A Heat Pump Water Heater working principle is very interesting as it produces hot water very differently than an electric water heater. How a heat pump works will be discussed in detail in this blog.
Table of Contents
Components of a heat pump
There are two main units of a heat pump water heater. The components of a heat pump are:
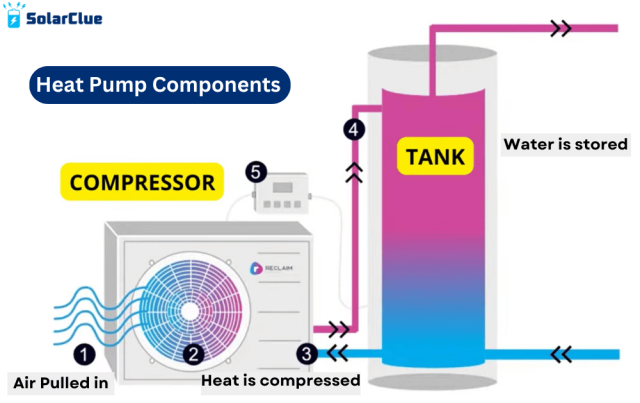
1. Compressor Unit
This unit collects heat from the surrounding air and compresses the heat. It has two parts, which are:
- Exhaust fan: This continuously extracts heat from the surrounding air.
- Refrigerant: This is the part of the compressor unit which compresses the heat to increases the heat.
2. Tank Unit
This is the unit where water is stored. This is where the heat is transferred after the refrigerant compresses the heat.
3. Electrical back-up coil
A heat pump has an electrical coil. This coil heats the water when the user manually fixes a higher temperature than 55°F. The electric coil starts working automatically when required, and when the work is over, it stops working automatically.
Step-by-step working principle of a heat pump
Let’s see how the heat pump system components work together to produce hot water efficiently.
Step 1:
Hot air is absorbed from the environment using the exhaust fan. The exhaust fan uses electricity. The exhaust fan needs to be turned on all the time, as it continuously needs to absorb heat from the surrounding air.
Step 2:
The heat that is absorbed by the exhaust fan is then transferred to the refrigerant. The refrigerant compresses the heat that is collected from the surrounding air. This is done because the heat collected from the outside is not more than 30°F. So, by compressing the heat, it increases the temperature.
This process continues, till the heat reaches the temperature, when hot water can be produced in the desired temperature.
Step 3:
After the heat is compressed, it is transferred to the tank unit. The tank has water stored in it. This water is transferred to hot water, using the heat.
Step 4:
The heat pump normally heats water up to55°F. But you can manually fix a temperature above 55°F. When a user fixes a temperature above that, the electric back-up coil automatically starts, and heats water as specified. It again stops working when the water reaches the specified temperature.
Conclusion
A heat pump water heater is 90% renewable. A heat pump works on electricity to produce hot water. But if compared to traditional water heaters, it does reduce energy consumption.
A heat pump may have high upfront costs, but it is cheaper in the long run, as it will save you bucks on your monthly electricity bills. Also, it has a longer life span. So, a heat pump is an ideal choice for your home.
Visit SolarClue® to see the best heat pump water heaters. SolarClue® is an online marketplace where solar energy products are sold at discounts up to 50%.




