On-Grid Solar: Definition and Key Features Explained
On-grid systems are designed to shut down during power outages to prevent sending electricity into the grid, ensuring the safety of utility workers.
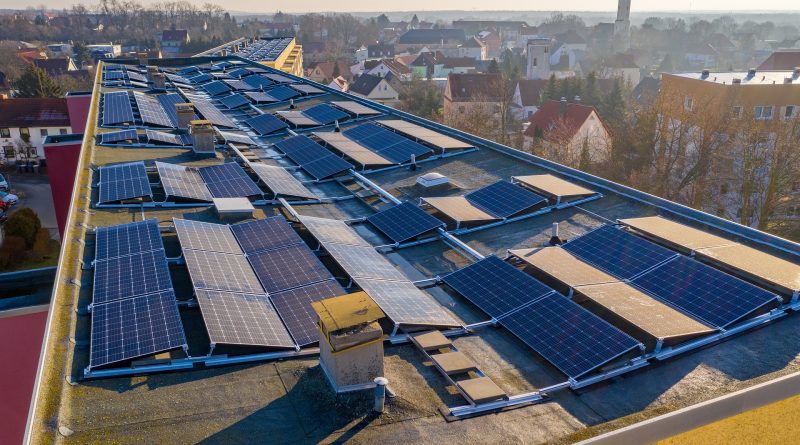
The main components include solar panels, inverters, mounting structures, grid connection equipment, and a solar meter.
Lean Startup Methodology Guide
On-grid solar power systems have gained significant popularity in recent years as a sustainable and cost-effective solution for generating electricity. By harnessing the sun’s energy and converting it into usable electricity, these systems offer numerous benefits to both individuals and the environment. In this blog, we will delve into the concept of on-grid solar power, exploring how it works, its advantages, and its potential impact on our daily lives.
Table of Contents
What is On-grid Solar?
On-grid solar, often referred to as grid-tied or grid-connected solar, is a photovoltaic system that operates in conjunction with the traditional power grid. Unlike off-grid systems that function independently, on-grid solar power systems utilize a connection to the local electrical utility grid. This connection allows users to both consume electricity from the grid and send any surplus electricity generated by their solar panels back to it.
On-grid solar setups comprise several key components. The solar panels, typically mounted on rooftops or other open spaces, capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. This DC power then passes through an inverter, which converts it into alternating current (AC) electricity, the type of electricity used in homes and businesses. The AC power is then distributed for use or fed into the grid.
How Does On-grid Solar Work?
The functionality of on-grid solar systems revolves around a method known as net metering. Net metering allows users to save on electricity bills by fully utilizing the energy generated by their solar panels while still maintaining a reliable connection to the grid.
When the sun is shining, and the solar panels generate more electricity than is being consumed, the excess energy is sent back to the grid via the inverter. This surplus electricity spins the electric meter backward, effectively crediting the user’s account for the energy exported. Conversely, during times when the solar system isn’t producing enough electricity to meet the user’s demand, electricity is drawn from the grid, and the meter moves forward accordingly.
At the end of a billing period, the electricity user is billed or credited based on the net difference between the electricity consumed and exported. This net metering arrangement ensures that users get value for the energy they produce and minimizes wastage of excess electricity.
The Advantages of On-grid Solar
1. Cost Savings: One of the primary advantages of on-grid solar is the potential for significant cost savings. By leveraging net metering, users can offset their electricity bills by exporting excess energy to the grid. Over time, this can result in substantial financial savings, especially in regions where electricity prices are high.
2. Environmental Benefits: On-grid solar power is a clean and renewable energy source, generating electricity without releasing harmful greenhouse gases or pollutants into the atmosphere. By utilizing solar energy, users contribute to a greener and more sustainable future.
3. Reliability: The connection to the grid ensures a reliable and uninterrupted supply of electricity, even during periods of insufficient solar generation. Users can rely on the grid as a backup, allowing for a seamless power supply without the need for expensive energy storage systems.
4. Low Maintenance: On-grid solar systems generally require minimal maintenance, as they do not rely on batteries or complex components. Regular cleaning of solar panels to maximize efficiency and occasional checks for faulty wiring or connections are typically sufficient to ensure optimal performance.
5. Flexibility: On-grid solar systems are highly scalable, making it easy to expand or modify the installation based on the user’s changing needs. Users can install additional panels or upgrade their system to accommodate increased energy requirements, enabling them to adapt to evolving electricity consumption patterns.
Conclusion
Illuminate your path to a sustainable future with SolarClue®’s on-grid solar systems. Offering a practical and eco-friendly solution for generating electricity by harnessing the sun’s energy, our systems feature net metering to offset your electricity bills. Enjoy the benefits of a reliable power supply, contribute to a cleaner environment, and take advantage of on-grid solar’s advantages, including cost savings, environmental benefits, reliability, low maintenance, and flexibility. Join the movement towards clean and sustainable energy – choose SolarClue® and power your life with the sun.
Frequently Asked Questions
On-grid solar, also known as grid-tied or grid-connected solar, refers to a solar power system that is connected to the local electrical grid.
Unlike off-grid systems, on-grid solar setups remain connected to the electrical grid, allowing users to draw power from the grid when solar production is low.
The main components include solar panels, inverters, mounting structures, grid connection equipment, and a solar meter.
Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity through the photovoltaic effect.
The inverter converts DC electricity from solar panels into alternating current (AC), making it compatible with the electrical grid and usable in homes and businesses.
Typically, on-grid systems do not use batteries for storage. Excess electricity is fed back into the grid, acting as a virtual storage system.
On-grid systems are designed to shut down during power outages to prevent sending electricity into the grid, ensuring the safety of utility workers.
Yes, on-grid systems can be easily expanded by adding more solar panels and inverters to increase capacity based on changing energy needs.
Net metering allows users to receive credits for excess electricity they contribute to the grid, reducing overall energy costs.
On-grid systems contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions by generating clean, renewable energy and promoting environmental sustainability.